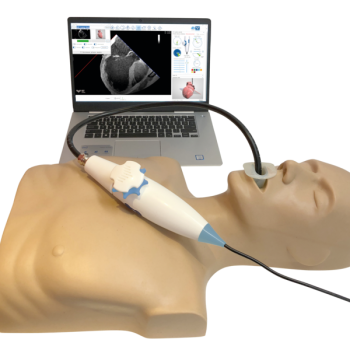
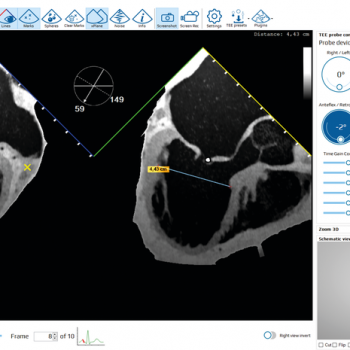
CALL OUR SALES TEAM FOR PRICING
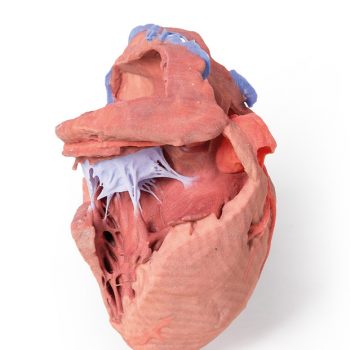
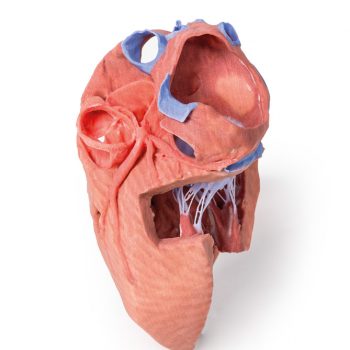
This heart model has been dissected to display the internal structures of the chambers. At the base of the heart the termination of the superior vena cava is preserved entering the right atrium. Part of the inferior vena cava is also preserved on the inferior aspect of the right atrium; however, most of the vessel lumen and much of the anterior wall has been removed to expose the pectinate muscles of the right auricle and the fossa ovalis (which is nearly translucent in the 3D print). The anterior wall of the right ventricle has also been removed to expose the right atrioventricular valve and its three cusps (anterior, posterior, and septal), including the chordae tendineae connecting them to respective papillary muscles projecting from trabeculae carneae (including a septomarginal trabecula entering the anterior papillary muscle from the interventricular septum). The smooth wall of the conus arteriosus is also exposed leading to the pulmonary semilunar valve (left, right, and anterior cusps) at the base of the pulmonary trunk. Preserved and encircling the right atrioventricular valve is the right coronary artery, ultimately passing to the posterior aspect and the origin of the posterior interventricular artery and atrioventricular nodal artery. On the posterior side of heart the terminations of the pulmonary veins are visible entering the opened left atrium. Just anterior to the depression of the fossa ovalis in the interatrial septum the left atrioventricular valve with its two cusps (anterior and posterior) is preserved, along with the associated chordae tendineae and papillary muscles in the ventricle. The walls of the opened left ventricle preserve well-developed trabeculae carneae. At the apex of the ventricle the aortic semilunar valve (with left, right, and posterior cusps preserved) can be seen at the base of the sectioned aorta alongside the origin of both coronary arteries. The left coronary artery in this specimen is very short, giving rise almost immediately from its origin to the left anterior descending artery, the diagonal artery, the ramus intermedius, and the circumflex branch. The latter branch passes between the left atrium and ventricle adjacent to the opened coronary sinus leading to the right atrium. The left anterior descending branch penetrates the myocardium in this individual and travels through the tissue, only emerging superficially to become visible again near the apex.